Instalando o Certificado HTTPS Nginx Free no Ubuntu Linux
Este tutorial mostrará todos os passos necessários para configurar os Blocos de Servidor Nginx no Ubuntu Linux.
O Nginx Server Blocks é praticamente o mesmo que o recurso de host Apache Virtual.
Este tutorial foi testado no Ubuntu 18.04.
1. Instale o Nginx no Ubuntu Linux
Use o comando APT do Ubuntu para instalar o servidor Nginx.
# apt-get update
# apt-get install nginx
Reinicie o servidor da Web Nginx manualmente.
# service nginx restart
# service nginx status
Verifique o status do serviço Nginx.
● nginx.service – A high performance web server and a reverse proxy server
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Sat 2018-12-29 04:29:22 UTC; 1h 17min ago
Docs: man:nginx(8)
Process: 2233 ExecStart=/usr/sbin/nginx -g daemon on; master_process on; (code=exited, status
Process: 2221 ExecStartPre=/usr/sbin/nginx -t -q -g daemon on; master_process on; (code=exite
Main PID: 2238 (nginx)
Tasks: 2 (limit: 1152)
CGroup: /system.slice/nginx.service
├─2238 nginx: master process /usr/sbin/nginx -g daemon on; master_process on;
└─2239 nginx: worker process
Você terminou a instalação do servidor Web Nginx no Ubuntu Linux.
2. Adicionar Suporte PHP ao Nginx
O Nginx precisa de um programa externo para adicionar suporte ao PHP.
Use o comando APT do Ubuntu para instalar os pacotes requeridos do PHP.
# apt-get update
# apt-get install php7.2-fpm
Opcional. Use o seguinte comando para instalar os módulos PHP mais usados.
# apt-get install php7.2-xml php7.2-curl php7.2-gd php7.2-mbstring php7.2-mysql
# apt-get install php7.2-bz2 php7.2-zip php7.2-json php7.2-readline
Encontre a localização do arquivo de configuração do PHP em seu sistema.
Edite o arquivo de configuração do php.ini.
# updatedb
# locate php.ini
# vi /etc/php/7.2/fpm/php.ini
Sua versão do PHP pode não ser a mesma que a nossa.
Seu local do arquivo de configuração do PHP pode não ser o mesmo que o nosso.
Aqui está o arquivo com nossa configuração.
file_uploads = On
max_execution_time = 300
memory_limit = 256M
post_max_size = 32M
max_input_time = 60
max_input_vars = 4440
upload_max_filesize = 32M
Edite o arquivo de configuração do site padrão do Nginx.
# vi /etc/nginx/sites-available/default
Aqui está o arquivo original, antes da nossa configuração.
server {
listen 80 default_server;
listen [::]:80 default_server;
root /var/www/html;
index index.html index.htm index.nginx-debian.html;
server_name _;
location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ =404;
}
}
Aqui está o novo arquivo com nossa configuração.
server {
listen 80 default_server;
listen [::]:80 default_server;
root /var/www/html;
index index.php index.html index.htm;
server_name _;
location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ =404;
}
location ~ .php$ {
include snippets/fastcgi-php.conf;
fastcgi_pass unix:/var/run/php/php7.2-fpm.sock;
}
}
Verifique se o seu arquivo de configuração do Nginx não tem erro.
# nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful
Reinicie o serviço PHP.
Reinicie o serviço Nginx.
# service php7.2-fpm restart
# service nginx restart
Você terminou a integração do Nginx com o PHP no Ubuntu Linux.
3. Configurar Blocos do Servidor Nginx
Blocos de servidores é um recurso que permite que um servidor Nginx ofereça vários sites usando o mesmo endereço IP.
Vamos criar a infra-estrutura necessária para usar o recurso de blocos do Servidor Nginx.
# mkdir /websites/mining-pool -p
# cd /websites/mining-pool
# mkdir www
# chown www-data.www-data /websites -R
Nosso site será chamado mining-pool.ninja.
Os arquivos do site mining-pool.ninja devem estar dentro do diretório / websites / mining-pool / www.
Alert!
You need to change your configuration files to reflect your website name.
Crie um arquivo de configuração Niganx Virtualhost em seu site.
# vi /etc/nginx/sites-available/mining-pool.conf
Aqui está o arquivo com nossa configuração.
server {
listen 80;
listen [::]:80;
root /websites/mining-pool/www;
index index.php index.html index.htm;
server_name mining-pool.ninja;
location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ =404;
}
location ~ .php$ {
include snippets/fastcgi-php.conf;
fastcgi_pass unix:/var/run/php/php7.2-fpm.sock;
}
}
Crie um link simbólico para ativar a configuração do host virtual Nginx.
Reinicie o serviço Nginx.
# ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/mining-pool.conf /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/
# service nginx restart
Você terminou a configuração do bloco Nginx Server.
4. Configurar o Domínio DNS
Acesse o GODADDY e compre um domínio DNS.
Em nosso exemplo, compramos o domínio chamado MINING-POOL.NINJA.
Você pode usar qualquer site para comprar um domínio DNS, o GoDaddy é apenas minha escolha pessoal.
Crie uma entrada DNS apontando seu site para o computador que está executando o Nginx.
Em nosso exemplo, criamos uma entrada de DNS apontando o domínio MINING-POOL.NINJA para o endereço IP 35.163.100.49.
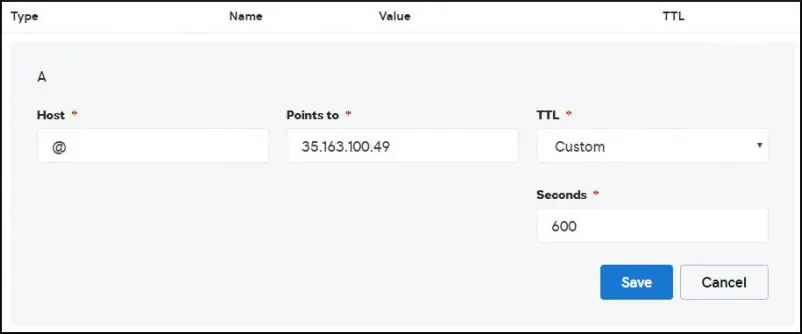
Use o comando NSLOOKUP para testar sua configuração de DNS
# apt-get update
# apt-get install dnsutils
# nslookup mining-pool.ninja
Non-authoritative answer:
Name: mining-pool.ninja
Address: 35.163.100.49
Você terminou a configuração do domínio DNS.
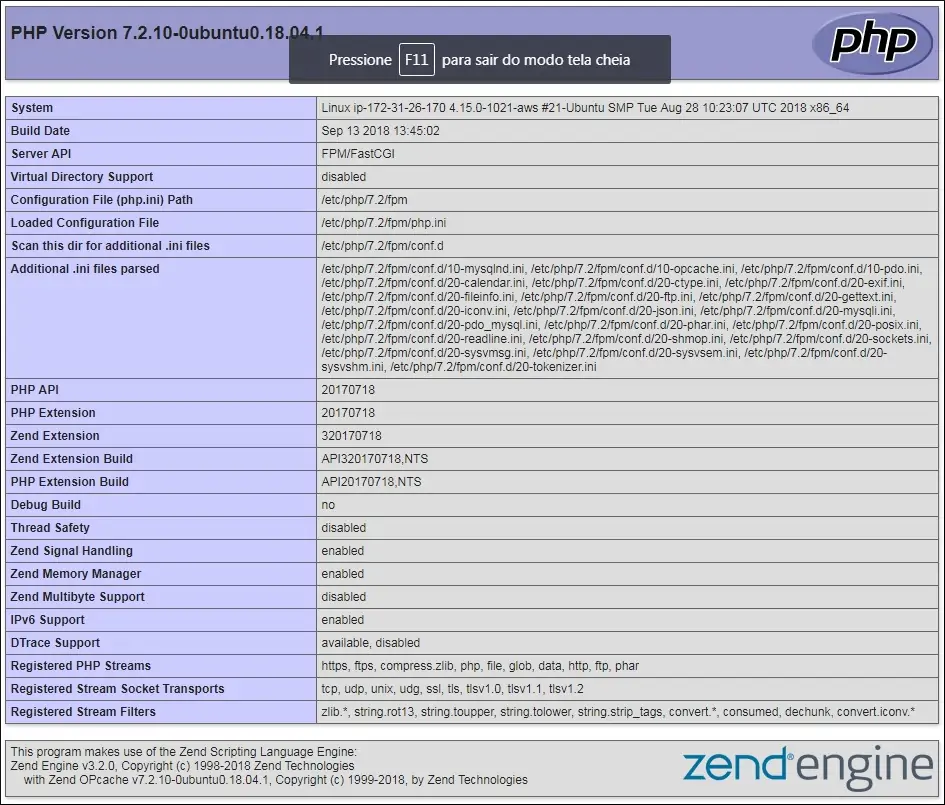
Para testar nossa configuração, vamos criar uma página básica de teste do PHP.
# vi /websites/mining-pool/www/index.php
Aqui está o conteúdo do arquivo index.php.
<?php phpinfo(); ?>
Abra seu navegador e tente acessar a versão HTTP do seu site.
Em nosso exemplo, o seguinte URL foi inserido no navegador:
• http://mining-pool.ninja
A página de informações do PHP deve ser apresentada.
5. Configurar o Free HTTPS Certificate no Nginx
Install the required packages to use the LET’S ENCRYPT Free SSL/TLS Certificates on Ubuntu Linux
# apt-get install software-properties-common
# add-apt-repository universe
# add-apt-repository ppa:certbot/certbot
# apt-get update
# apt-get install python-certbot-nginx
Solicite e instale o certificado HTTPS gratuito do Nginx.
certbot –nginx -d mining-pool.ninja
• Pressione (A) para concordar com os Termos de Serviço.
• Pressione (Y) para compartilhar seu e-mail e receber Newsletters.
• Pressione (2) para redirecionar automaticamente seu site HTTP para as versões HTTPS.
Saving debug log to /var/log/letsencrypt/letsencrypt.log
Plugins selected: Authenticator nginx, Installer nginx
Enter email address (used for urgent renewal and security notices) (Enter ‘c’ to
cancel): techexpert.tips@gmail.com
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
Please read the Terms of Service at
https://letsencrypt.org/documents/LE-SA-v1.2-November-15-2017.pdf. You must
agree in order to register with the ACME server at
https://acme-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
(A)gree/(C)ancel: A
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
Would you be willing to share your email address with the Electronic Frontier
Foundation, a founding partner of the Let’s Encrypt project and the non-profit
organization that develops Certbot? We’d like to send you email about our work
encrypting the web, EFF news, campaigns, and ways to support digital freedom.
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
(Y)es/(N)o: Y
Obtaining a new certificate
Performing the following challenges:
http-01 challenge for mining-pool.ninja
Waiting for verification…
Cleaning up challenges
Deploying Certificate to VirtualHost /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/mining-pool.conf
Please choose whether or not to redirect HTTP traffic to HTTPS, removing HTTP access.
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
1: No redirect – Make no further changes to the webserver configuration.
2: Redirect – Make all requests redirect to secure HTTPS access. Choose this for
new sites, or if you’re confident your site works on HTTPS. You can undo this
change by editing your web server’s configuration.
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
Select the appropriate number [1-2] then [enter] (press ‘c’ to cancel): 2
Redirecting all traffic on port 80 to ssl in /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/mining-pool.conf
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
Congratulations! You have successfully enabled https://mining-pool.ninja
You should test your configuration at:
https://www.ssllabs.com/ssltest/analyze.html?d=mining-pool.ninja
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
IMPORTANT NOTES:
– Congratulations! Your certificate and chain have been saved at:
/etc/letsencrypt/live/mining-pool.ninja/fullchain.pem
Your key file has been saved at:
/etc/letsencrypt/live/mining-pool.ninja/privkey.pem
Your cert will expire on 2019-03-31. To obtain a new or tweaked
version of this certificate in the future, simply run certbot again
with the “certonly” option. To non-interactively renew *all* of
your certificates, run “certbot renew”
– Your account credentials have been saved in your Certbot
configuration directory at /etc/letsencrypt. You should make a
secure backup of this folder now. This configuration directory will
also contain certificates and private keys obtained by Certbot so
making regular backups of this folder is ideal.
– If you like Certbot, please consider supporting our work by:
Donating to ISRG / Let’s Encrypt: https://letsencrypt.org/donate
Donating to EFF: https://eff.org/donate-le
O sistema solicitará automaticamente o certificado gratuito.
Ele também configurará seu servidor da Web Nginx para redirecionar todo o acesso HTTP à versão HTTPS do seu site.
Em nosso exemplo, o sistema modificou o arquivo de configuração do Virtualhost chamado mining-pool.conf.
Aqui está o conteúdo do arquivo modificado mining-pool.conf.
server {
root /websites/mining-pool/www;
index index.php index.html index.htm;
server_name mining-pool.ninja;
location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ =404;
}
location ~ .php$ {
include snippets/fastcgi-php.conf;
fastcgi_pass unix:/var/run/php/php7.2-fpm.sock;
}
listen [::]:443 ssl ipv6only=on; # managed by Certbot
listen 443 ssl; # managed by Certbot
ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/mining-pool.ninja/fullchain.pem; # managed by Certbot
ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/live/mining-pool.ninja/privkey.pem; # managed by Certbot
include /etc/letsencrypt/options-ssl-nginx.conf; # managed by Certbot
ssl_dhparam /etc/letsencrypt/ssl-dhparams.pem; # managed by Certbot
}
server {
if ($host = mining-pool.ninja) {
return 301 https://$host$request_uri;
} # managed by Certbot
listen 80;
listen [::]:80;
server_name mining-pool.ninja;
return 404; # managed by Certbot
}
O arquivo KEY contém sua chave privada do Certificado e deve ser mantido em um local seguro o tempo todo.
O arquivo de chave para mining-pool.ninja foi armazenado em /etc/letsencrypt/live/mining-pool.ninja/privkey.pem.
6. Teste o Free HTTPS Certificate no Nginx
Toda a configuração necessária está concluída.
Está na hora de testar sua configuração.
Abra seu navegador e tente acessar a versão HTTP do seu site.
Em nosso exemplo, o seguinte URL foi inserido no navegador:
• http://mining-pool.ninja
O Nginx redirecionará automaticamente a solicitação HTTP para a versão HTTPS do seu site.
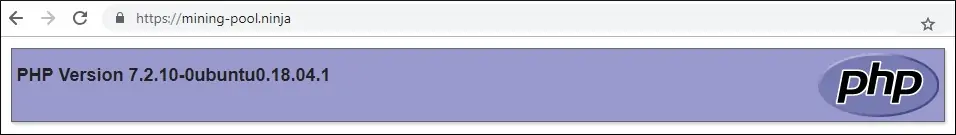
Você concluiu a configuração do certificado gratuito Nginx HTTPS.
7. Como Renovar o Free HTTPS Certificate
Os Certificados LET’S ENCRYPT Free SSL / TLS são válidos apenas por 90 dias.
O sistema cria uma tarefa agendada para renovar automaticamente qualquer certificado dentro de trinta dias após a expiração.
O nome da tarefa agendada é certbot e está localizado dentro do diretório /etc/cron.d.
Aqui está o conteúdo do arquivo /etc/cron.d/certbot:
# /etc/cron.d/certbot: crontab entries for the certbot package
#
# Upstream recommends attempting renewal twice a day
#
# Eventually, this will be an opportunity to validate certificates
# haven’t been revoked, etc. Renewal will only occur if expiration
# is within 30 days.
#
# Important Note! This cronjob will NOT be executed if you are
# running systemd as your init system. If you are running systemd,
# the cronjob.timer function takes precedence over this cronjob. For
# more details, see the systemd.timer manpage, or use systemctl show
# certbot.timer.
SHELL=/bin/sh
PATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin
0 */12 * * * root test -x /usr/bin/certbot -a ! -d /run/systemd/system && perl -e ‘sleep int(rand(43200))’ && certbot -q renew
Use o seguinte comando para simular o processo de renovação do certificado.
# certbot renew –dry-run
Você deve ver as seguintes mensagens:
Saving debug log to /var/log/letsencrypt/letsencrypt.log
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
Processing /etc/letsencrypt/renewal/mining-pool.ninja.conf
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
Cert not due for renewal, but simulating renewal for dry run
Plugins selected: Authenticator nginx, Installer nginx
Renewing an existing certificate
Performing the following challenges:
http-01 challenge for mining-pool.ninja
Waiting for verification…
Cleaning up challenges
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
new certificate deployed with reload of nginx server; fullchain is
/etc/letsencrypt/live/mining-pool.ninja/fullchain.pem
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
** DRY RUN: simulating ‘certbot renew’ close to cert expiry
** (The test certificates below have not been saved.)
Congratulations, all renewals succeeded. The following certs have been renewed:
/etc/letsencrypt/live/mining-pool.ninja/fullchain.pem (success)
** DRY RUN: simulating ‘certbot renew’ close to cert expiry
** (The test certificates above have not been saved.)
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –

Leave A Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.