Installieren des Apache Free HTTPS-Zertifikats unter Ubuntu Linux
Dieses Tutorial zeigt Ihnen alle Schritte, die zur Installation des Apache Free HTTPS-Zertifikats unter Ubuntu Linux erforderlich sind.
Inhaltsverzeichnis
Apache unter Ubuntu Linux Installieren
Lassen Sie uns Apache mit der richtigen PHP-Unterstützung installieren.
Verwenden Sie den Ubuntu APT-Befehl, um den Apache-Server zu installieren.
# apt-get update
# apt-get install apache2 php7.2 php7.2-mysql libapache2-mod-php7.2
# service apache2 restart
Wahlweise. Verwenden Sie den folgenden Befehl, um die am häufigsten verwendeten Apache-Module von Apache zu installieren.
# apt-get install php7.2-xml php7.2-curl php7.2-gd php7.2-mbstring
# apt-get install php7.2-bz2 php7.2-zip php7.2-json php7.2-readline
Aktivieren Sie Apache mod_ssl.
Aktivieren Sie Apache mod_rewrite.
Bearbeiten Sie die Datei apache2.conf.
# a2enmod ssl
# a2enmod rewrite
# vi /etc/apache2/apache2.conf
Fügen Sie am Ende von apache2.conf die folgenden Zeilen hinzu
<Directory /var/www/html>
AllowOverride All
</Directory>
Starten Sie den Apache-Dienst neu.
# service apache2 restart
Sie haben die Installation des Apache-Webservers unter Ubuntu Linux abgeschlossen.
Konfigurieren der Virtuellen Apache-Hosts
Virtuelle Hosts: Eine Funktion, mit der ein Apache-Server mehrere Websites mit derselben IP-Adresse anbieten kann.
Lassen Sie uns die notwendige Infrastruktur für die Verwendung der Apache VirtualHosts-Funktion erstellen.
# mkdir /websites/mining-pool
# cd /websites/mining-pool
# mkdir www logs
# chown www-data.www-data /websites -R
Unsere Website heißt mining-pool.ninja.
Die Dateien für die mining-pool.ninja-Website sollten sich im Verzeichnis / websites / mining-pool / www befinden.
Die Mining- Pool.ninja-Protokolle werden im Verzeichnis / websites / mining-pool / logs gespeichert.
Alert!
You need to change your configuration files to reflect your website name.
Erstellen Sie eine Apache Virtualhost-Konfigurationsdatei für Ihre Website.
# vi /etc/apache2/sites-available/mining-pool.conf
Hier ist die Datei mit unserer Konfiguration.
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerAdmin nobody@care.com
DocumentRoot /websites/mining-pool/www
ServerName mining-pool.ninja
<Directory /websites/mining-pool/www/>
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks
AllowOverride All
Require all granted
</Directory>
ErrorLog /websites/mining-pool/logs/error.log
CustomLog /websites/mining-pool/logs/access.log combined
LogLevel error
</VirtualHost>
Aktivieren Sie Ihre Website Virtualhost-Konfigurationsdatei.
Starten Sie den Apache-Dienst neu.
# a2ensite mining-pool.conf
# service apache2 restart
Sie haben die Konfiguration von Apache VirtualHosts abgeschlossen.
Konfigurieren der DNS-Domänenregistrierung
Greife auf GODADDY und erwerben Sie eine DNS-Domäne.
In unserem Beispiel erwerben wir die Domäne MINING-POOL.NINJA.
Sie können jede Website zum Kauf einer DNS-Domäne verwenden. GoDaddy ist nur meine persönliche Entscheidung.
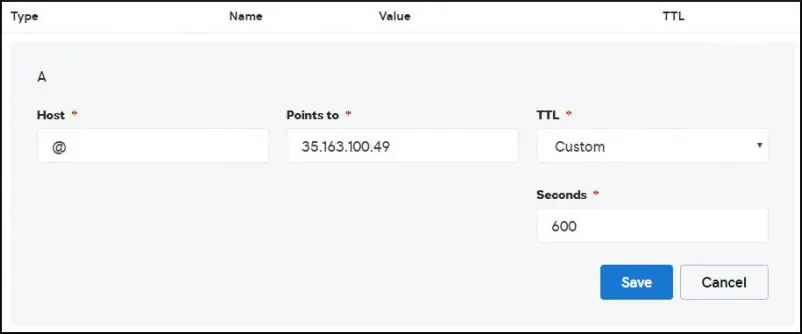
Erstellen Sie einen DNS-Eintrag, der Ihre Website auf den Computer zeigt, auf dem Apache ausgeführt wird.
In unserem Beispiel haben wir einen DNS-Eintrag erstellt, der die Domäne MINING-POOL.NINJA auf die IP-Adresse 35.163.100.49 verweist.
Verwenden Sie den Befehl NSLOOKUP, um Ihre DNS-Konfiguration zu testen
# apt-get update
# apt-get install dnsutils
# nslookup mining-pool.ninja
Non-authoritative answer:
Name: mining-pool.ninja
Address: 35.163.100.49
Sie haben die DNS-Domänenkonfiguration abgeschlossen.
Öffnen Sie Ihren Browser und versuchen Sie, auf die HTTP-Version Ihrer Website zuzugreifen.
In unserem Beispiel wurde die folgende URL in den Browser eingegeben:
• http://mining-pool.ninja
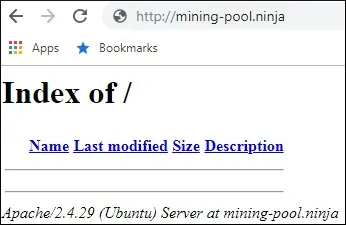
Jetzt besteht unser einziges Problem darin, das kostenlose HTTPS-Zertifikat zu installieren und den gesamten HTTP-Verkehr automatisch auf die HTTPS-Version unserer Website umzuleiten.
Konfigurieren des Kostenlosen HTTPS-Zertifikats für Apache
Installieren Sie die erforderlichen Pakete, um die LET’S ENCRYPT Free SSL / TLS-Zertifikate unter Ubuntu Linux zu verwenden
# apt-get install software-properties-common
# add-apt-repository universe
# add-apt-repository ppa:certbot/certbot
# apt-get update
# apt-get install python-certbot-apache
Fordern Sie das Apache free HTTPS-Zertifikat an und installieren Sie es.
# certbot –apache -d mining-pool.ninja
• Drücken Sie (A), um die Nutzungsbedingungen zu akzeptieren.
• Drücken Sie (J), um Ihre E-Mail zu teilen und Newsletter zu erhalten.
• Drücken Sie (2), um Ihre HTTP-Website automatisch zu den HTTPS-Versionen umzuleiten.
Saving debug log to /var/log/letsencrypt/letsencrypt.log
Plugins selected: Authenticator apache, Installer apache
Enter email address (used for urgent renewal and security notices) (Enter ‚c‘ to
cancel): techexpert.tips@gmail.com
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
Please read the Terms of Service at
https://letsencrypt.org/documents/LE-SA-v1.2-November-15-2017.pdf. You must
agree in order to register with the ACME server at
https://acme-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
(A)gree/(C)ancel: A
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
Would you be willing to share your email address with the Electronic Frontier
Foundation, a founding partner of the Let’s Encrypt project and the non-profit
organization that develops Certbot? We’d like to send you email about our work
encrypting the web, EFF news, campaigns, and ways to support digital freedom.
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
(Y)es/(N)o: Y
Obtaining a new certificate
Performing the following challenges:
http-01 challenge for mining-pool.ninja
Enabled Apache rewrite module
Waiting for verification…
Cleaning up challenges
Created an SSL vhost at /etc/apache2/sites-available/mining-pool-le-ssl.conf
Enabled Apache socache_shmcb module
Enabled Apache ssl module
Deploying Certificate to VirtualHost /etc/apache2/sites-available/mining-pool-le-ssl.conf
Enabling available site: /etc/apache2/sites-available/mining-pool-le-ssl.conf
Please choose whether or not to redirect HTTP traffic to HTTPS, removing HTTP access.
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
1: No redirect – Make no further changes to the webserver configuration.
2: Redirect – Make all requests redirect to secure HTTPS access. Choose this for
new sites, or if you’re confident your site works on HTTPS. You can undo this
change by editing your web server’s configuration.
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
Select the appropriate number [1-2] then [enter] (press ‚c‘ to cancel): 2
Enabled Apache rewrite module
Redirecting vhost in /etc/apache2/sites-enabled/mining-pool.conf to ssl vhost in /etc/apache2/sites-available/mining-pool-le-ssl.conf
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
Congratulations! You have successfully enabled https://mining-pool.ninja
You should test your configuration at:
https://www.ssllabs.com/ssltest/analyze.html?d=mining-pool.ninja
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
IMPORTANT NOTES:
– Congratulations! Your certificate and chain have been saved at:
/etc/letsencrypt/live/mining-pool.ninja/fullchain.pem
Your key file has been saved at:
/etc/letsencrypt/live/mining-pool.ninja/privkey.pem
Your cert will expire on 2019-03-19. To obtain a new or tweaked
version of this certificate in the future, simply run certbot again
with the „certonly“ option. To non-interactively renew *all* of
your certificates, run „certbot renew“
– If you like Certbot, please consider supporting our work by:
Donating to ISRG / Let’s Encrypt: https://letsencrypt.org/donate
Donating to EFF: https://eff.org/donate-le
Das System fordert automatisch das kostenlose Zertifikat an.
Außerdem wird Ihr Apache-Webserver so konfiguriert, dass der gesamte HTTP-Zugriff auf die HTTPS-Version Ihrer Website umgeleitet wird.
In unserem Beispiel hat das System eine HTTPS Virtualhost-Konfigurationsdatei mit dem Namen mining-pool-le-ssl.conf erstellt
Hier ist der Inhalt der HTTPS Virtualhost-Konfigurationsdatei mining-pool-le-ssl.conf:
<IfModule mod_ssl.c>
<VirtualHost *:443>
ServerAdmin nobody@care.com
DocumentRoot /websites/www
ServerName mining-pool.ninja
<Directory /websites/www/>
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks
AllowOverride All
Require all granted
</Directory>
ErrorLog /websites/logs/error.log
CustomLog /websites/logs/access.log combined
LogLevel error
SSLCertificateFile /etc/letsencrypt/live/mining-pool.ninja/fullchain.pem
SSLCertificateKeyFile /etc/letsencrypt/live/mining-pool.ninja/privkey.pem
Include /etc/letsencrypt/options-ssl-apache.conf
</VirtualHost>
</IfModule>
Die KEY-Datei enthält Ihren privaten Zertifikatschlüssel und muss immer an einem sicheren Ort aufbewahrt werden.
Die Schlüsseldatei zu mining-pool.ninja wurde unter /etc/letsencrypt/live/mining-pool.ninja/privkey.pem gespeichert.
Das System ändert automatisch die ursprüngliche Konfigurationsdatei von Apache Virtualhost.
Alle HTTP-Anforderungen werden automatisch an die HTTPS-Version Ihrer Website umgeleitet.
Hier ist der Inhalt der aktualisierten ursprünglichen HTTP-Virtualhost-Konfigurationsdatei, mining-pool.conf:
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerAdmin nobody@care.com
DocumentRoot /websites/www
ServerName mining-pool.ninja
<Directory /websites/www/>
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks
AllowOverride All
Require all granted
</Directory>
ErrorLog /websites/logs/error.log
CustomLog /websites/logs/access.log combined
LogLevel error
RewriteEngine on
RewriteCond %{SERVER_NAME} =mining-pool.ninja
RewriteRule ^ https://%{SERVER_NAME}%{REQUEST_URI} [END,NE,R=permanent]
</VirtualHost>
Testen des Kostenlosen HTTPS-Zertifikats auf Apache
Die gesamte Konfiguration ist abgeschlossen.
Es ist an der Zeit, Ihre Konfiguration zu testen.
Öffnen Sie Ihren Browser und versuchen Sie, auf die HTTP-Version Ihrer Website zuzugreifen.
In unserem Beispiel wurde die folgende URL in den Browser eingegeben:
• http://mining-pool.ninja
Apache leitet die HTTP-Anforderung automatisch an die HTTPS-Version Ihrer Website um.
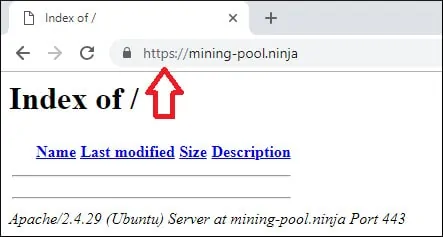
Sie haben die Konfiguration des kostenlosen Apache HTTPS-Zertifikats abgeschlossen.
So Erneuern Sie das Kostenlose HTTPS-Zertifikat
Die kostenlosen SSL / TLS-Zertifikate von LET’S ENCRYPT sind nur 90 Tage gültig.
Das System erstellt eine geplante Aufgabe, um ein Zertifikat innerhalb von dreißig Tagen nach Ablauf automatisch zu erneuern.
Der Name der geplanten Task ist certbot und befindet sich im Verzeichnis /etc/cron.d.
Hier ist der Inhalt der Datei /etc/cron.d/certbot:
# /etc/cron.d/certbot: crontab entries for the certbot package
#
# Upstream recommends attempting renewal twice a day
#
# Eventually, this will be an opportunity to validate certificates
# haven’t been revoked, etc. Renewal will only occur if expiration
# is within 30 days.
#
# Important Note! This cronjob will NOT be executed if you are
# running systemd as your init system. If you are running systemd,
# the cronjob.timer function takes precedence over this cronjob. For
# more details, see the systemd.timer manpage, or use systemctl show
# certbot.timer.
SHELL=/bin/sh
PATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin
0 */12 * * * root test -x /usr/bin/certbot -a ! -d /run/systemd/system && perl -e ’sleep int(rand(43200))‘ && certbot -q renew
Verwenden Sie den folgenden Befehl, um den Prozess der Zertifikatserneuerung zu simulieren.
# certbot renew –dry-run
Sie sollten die folgenden Meldungen sehen:
Saving debug log to /var/log/letsencrypt/letsencrypt.log
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
Processing /etc/letsencrypt/renewal/mining-pool.ninja.conf
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
Cert not due for renewal, but simulating renewal for dry run
Plugins selected: Authenticator apache, Installer apache
Renewing an existing certificate
Performing the following challenges:
http-01 challenge for mining-pool.ninja
Waiting for verification…
Cleaning up challenges
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
new certificate deployed with reload of apache server; fullchain is
/etc/letsencrypt/live/mining-pool.ninja/fullchain.pem
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
** DRY RUN: simulating ‚certbot renew‘ close to cert expiry
** (The test certificates below have not been saved.)
Congratulations, all renewals succeeded. The following certs have been renewed:
/etc/letsencrypt/live/mining-pool.ninja/fullchain.pem (success)
** DRY RUN: simulating ‚certbot renew‘ close to cert expiry
** (The test certificates above have not been saved.)
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
IMPORTANT NOTES:
– Your account credentials have been saved in your Certbot
configuration directory at /etc/letsencrypt. You should make a
secure backup of this folder now. This configuration directory will
also contain certificates and private keys obtained by Certbot so
making regular backups of this folder is ideal.
Leave A Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.