Installing Apache Free HTTPS Certificate on Ubuntu Linux
This tutorial will show you all the steps required to install Apache Free HTTPS Certificate on Ubuntu Linux.
Installing Apache on Ubuntu Linux
Let’s install Apache with proper PHP support.
Use the Ubuntu APT command to install the Apache server.
# apt-get update
# apt-get install apache2 php7.2 php7.2-mysql libapache2-mod-php7.2
# service apache2 restart
Optional. Use the following command to install the Apache most used PHP modules.
# apt-get install php7.2-xml php7.2-curl php7.2-gd php7.2-mbstring
# apt-get install php7.2-bz2 php7.2-zip php7.2-json php7.2-readline
Enable Apache mod_ssl.
Enable Apache mod_rewrite.
Edit the apache2.conf file.
# a2enmod ssl
# a2enmod rewrite
# vi /etc/apache2/apache2.conf
Add the following lines at the end of apache2.conf
<Directory /var/www/html>
AllowOverride All
</Directory>
Restart the Apache service.
# service apache2 restart
You finished the Apache Web server installation on Ubuntu Linux.
Configuring Apache Virtual Hosts
Virtual Hosts if a feature that allows one Apache server to offer multiple websites using the same IP address.
Lets’ create the necessary infrastructure to use the Apache VirtualHosts feature.
# mkdir /websites/mining-pool
# cd /websites/mining-pool
# mkdir www logs
# chown www-data.www-data /websites -R
Our website will be named mining-pool.ninja.
The mining-pool.ninja website files should be inside the /websites/mining-pool/www directory.
The mining-pool.ninja logs will be stored inside the /websites/mining-pool/logs directory.
Alert!
You need to change your configuration files to reflect your website name.
Create an Apache Virtualhost configuration file to your website.
# vi /etc/apache2/sites-available/mining-pool.conf
Here is the file with our configuration.
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerAdmin nobody@care.com
DocumentRoot /websites/mining-pool/www
ServerName mining-pool.ninja
<Directory /websites/mining-pool/www/>
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks
AllowOverride All
Require all granted
</Directory>
ErrorLog /websites/mining-pool/logs/error.log
CustomLog /websites/mining-pool/logs/access.log combined
LogLevel error
</VirtualHost>
Enable your Website Virtualhost configuration file.
Restart the Apache service.
# a2ensite mining-pool.conf
# service apache2 restart
You finished the Apache VirtualHosts configuration.
Configuring The DNS Domain Registry
Access the GODADDY WEBSITE and purchase a DNS domain.
In our example, we purchase the domain named MINING-POOL.NINJA.
You can use any website to purchase a DNS domain, GoDaddy is just my personal choice.
Create a DNS entry pointing your website to the computer running Apache.
In our example, we created a DNS entry pointing the domain MINING-POOL.NINJA to the IP address 35.163.100.49.
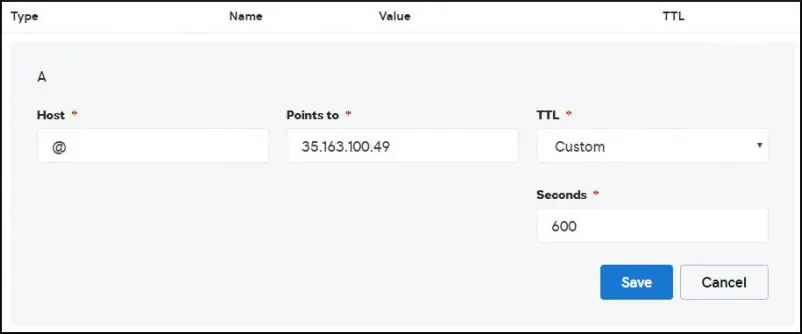
Use the NSLOOKUP command to test your DNS configuration
# apt-get update
# apt-get install dnsutils
# nslookup mining-pool.ninja
Non-authoritative answer:
Name: mining-pool.ninja
Address: 35.163.100.49
You finished the DNS domain configuration.
Open your browser and try to access the HTTP version of your website.
In our example, the following URL was entered in the Browser:
• http://mining-pool.ninja
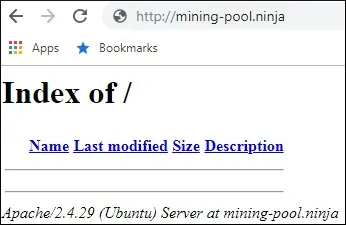
Now, our only concern is to install the free HTTPS certificate and redirect all HTTP traffic to the HTTPS version of our website automatically.
Configuring The Free HTTPS Certificate on Apache
Install the required packages to use the LET’S ENCRYPT Free SSL/TLS Certificates on Ubuntu Linux
# apt-get install software-properties-common
# add-apt-repository universe
# add-apt-repository ppa:certbot/certbot
# apt-get update
# apt-get install python-certbot-apache
Request and install the Apache free HTTPS certificate.
# certbot –apache -d mining-pool.ninja
• Press (A) to Agree with the Terms of Service.
• Press (Y) to share your e-mail and receive Newsletters.
• Press (2) to automatically redirect your HTTP website to the HTTPS versions.
Saving debug log to /var/log/letsencrypt/letsencrypt.log
Plugins selected: Authenticator apache, Installer apache
Enter email address (used for urgent renewal and security notices) (Enter ‘c’ to
cancel): techexpert.tips@gmail.com
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
Please read the Terms of Service at
https://letsencrypt.org/documents/LE-SA-v1.2-November-15-2017.pdf. You must
agree in order to register with the ACME server at
https://acme-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
(A)gree/(C)ancel: A
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
Would you be willing to share your email address with the Electronic Frontier
Foundation, a founding partner of the Let’s Encrypt project and the non-profit
organization that develops Certbot? We’d like to send you email about our work
encrypting the web, EFF news, campaigns, and ways to support digital freedom.
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
(Y)es/(N)o: Y
Obtaining a new certificate
Performing the following challenges:
http-01 challenge for mining-pool.ninja
Enabled Apache rewrite module
Waiting for verification…
Cleaning up challenges
Created an SSL vhost at /etc/apache2/sites-available/mining-pool-le-ssl.conf
Enabled Apache socache_shmcb module
Enabled Apache ssl module
Deploying Certificate to VirtualHost /etc/apache2/sites-available/mining-pool-le-ssl.conf
Enabling available site: /etc/apache2/sites-available/mining-pool-le-ssl.conf
Please choose whether or not to redirect HTTP traffic to HTTPS, removing HTTP access.
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
1: No redirect – Make no further changes to the webserver configuration.
2: Redirect – Make all requests redirect to secure HTTPS access. Choose this for
new sites, or if you’re confident your site works on HTTPS. You can undo this
change by editing your web server’s configuration.
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
Select the appropriate number [1-2] then [enter] (press ‘c’ to cancel): 2
Enabled Apache rewrite module
Redirecting vhost in /etc/apache2/sites-enabled/mining-pool.conf to ssl vhost in /etc/apache2/sites-available/mining-pool-le-ssl.conf
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
Congratulations! You have successfully enabled https://mining-pool.ninja
You should test your configuration at:
https://www.ssllabs.com/ssltest/analyze.html?d=mining-pool.ninja
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
IMPORTANT NOTES:
– Congratulations! Your certificate and chain have been saved at:
/etc/letsencrypt/live/mining-pool.ninja/fullchain.pem
Your key file has been saved at:
/etc/letsencrypt/live/mining-pool.ninja/privkey.pem
Your cert will expire on 2019-03-19. To obtain a new or tweaked
version of this certificate in the future, simply run certbot again
with the “certonly” option. To non-interactively renew *all* of
your certificates, run “certbot renew”
– If you like Certbot, please consider supporting our work by:
Donating to ISRG / Let’s Encrypt: https://letsencrypt.org/donate
Donating to EFF: https://eff.org/donate-le
The system will automatically request the free certificate.
It will also configure your Apache web server to redirect all HTTP access to the HTTPS version of your website.
In our example, the system created an HTTPS Virtualhost configuration file named mining-pool-le-ssl.conf
Here is the content of the HTTPS Virtualhost configuration file mining-pool-le-ssl.conf:
<IfModule mod_ssl.c>
<VirtualHost *:443>
ServerAdmin nobody@care.com
DocumentRoot /websites/www
ServerName mining-pool.ninja
<Directory /websites/www/>
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks
AllowOverride All
Require all granted
</Directory>
ErrorLog /websites/logs/error.log
CustomLog /websites/logs/access.log combined
LogLevel error
SSLCertificateFile /etc/letsencrypt/live/mining-pool.ninja/fullchain.pem
SSLCertificateKeyFile /etc/letsencrypt/live/mining-pool.ninja/privkey.pem
Include /etc/letsencrypt/options-ssl-apache.conf
</VirtualHost>
</IfModule>
The KEY file contains your Certificate private key and must be kept in a safe place all the time.
The key file to mining-pool.ninja was stored at /etc/letsencrypt/live/mining-pool.ninja/privkey.pem.
The system automatically modify the original Apache Virtualhost configuration file.
It will automatically redirect all HTTP requests to the HTTPS version of your website.
Here is the content of the updated original HTTP Virtualhost configuration file, mining-pool.conf:
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerAdmin nobody@care.com
DocumentRoot /websites/www
ServerName mining-pool.ninja
<Directory /websites/www/>
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks
AllowOverride All
Require all granted
</Directory>
ErrorLog /websites/logs/error.log
CustomLog /websites/logs/access.log combined
LogLevel error
RewriteEngine on
RewriteCond %{SERVER_NAME} =mining-pool.ninja
RewriteRule ^ https://%{SERVER_NAME}%{REQUEST_URI} [END,NE,R=permanent]
</VirtualHost>
Testing the Free HTTPS Certificate on Apache
All the configuration required is done.
It is time to test your configuration.
Open your browser and try to access the HTTP version of your website.
In our example, the following URL was entered in the Browser:
• http://mining-pool.ninja
Apache will automatically redirect the HTTP request to the HTTPS version of your website.
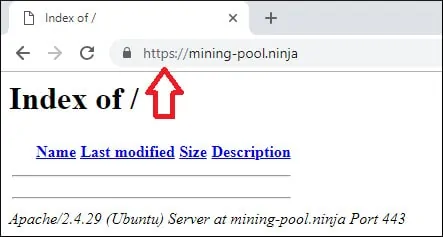
You finished the Apache HTTPS free certificate configuration.
How to Renew The Free HTTPS Certificate
The LET’S ENCRYPT Free SSL/TLS Certificates is valid only for 90 days.
The System creates a scheduled task to automatically renew any certificate within thirty days of expiration.
The scheduled task name is certbot and it is located inside the directory /etc/cron.d.
Here is the content of the /etc/cron.d/certbot file:
# /etc/cron.d/certbot: crontab entries for the certbot package
#
# Upstream recommends attempting renewal twice a day
#
# Eventually, this will be an opportunity to validate certificates
# haven’t been revoked, etc. Renewal will only occur if expiration
# is within 30 days.
#
# Important Note! This cronjob will NOT be executed if you are
# running systemd as your init system. If you are running systemd,
# the cronjob.timer function takes precedence over this cronjob. For
# more details, see the systemd.timer manpage, or use systemctl show
# certbot.timer.
SHELL=/bin/sh
PATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin
0 */12 * * * root test -x /usr/bin/certbot -a \! -d /run/systemd/system && perl -e ‘sleep int(rand(43200))’ && certbot -q renew
Use the following command to simulate the process of certificate renew.
# certbot renew –dry-run
You should see the following messages:
Saving debug log to /var/log/letsencrypt/letsencrypt.log
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
Processing /etc/letsencrypt/renewal/mining-pool.ninja.conf
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
Cert not due for renewal, but simulating renewal for dry run
Plugins selected: Authenticator apache, Installer apache
Renewing an existing certificate
Performing the following challenges:
http-01 challenge for mining-pool.ninja
Waiting for verification…
Cleaning up challenges
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
new certificate deployed with reload of apache server; fullchain is
/etc/letsencrypt/live/mining-pool.ninja/fullchain.pem
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
** DRY RUN: simulating ‘certbot renew’ close to cert expiry
** (The test certificates below have not been saved.)
Congratulations, all renewals succeeded. The following certs have been renewed:
/etc/letsencrypt/live/mining-pool.ninja/fullchain.pem (success)
** DRY RUN: simulating ‘certbot renew’ close to cert expiry
** (The test certificates above have not been saved.)
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
IMPORTANT NOTES:
– Your account credentials have been saved in your Certbot
configuration directory at /etc/letsencrypt. You should make a
secure backup of this folder now. This configuration directory will
also contain certificates and private keys obtained by Certbot so
making regular backups of this folder is ideal.
Leave A Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.