Installation du Certificat HTTPS Apache Free sur Ubuntu Linux
Ce tutoriel vous montrera toutes les étapes nécessaires à l’installation du certificat Apache Free HTTPS sur Ubuntu Linux.
Installer Apache sur Ubuntu Linux
Installons Apache avec le support PHP approprié.
Utilisez la commande Ubuntu APT pour installer le serveur Apache.
# apt-get update
# apt-get install apache2 php7.2 php7.2-mysql libapache2-mod-php7.2
# service apache2 restart
Optionnel. Utilisez la commande suivante pour installer les modules PHP les plus utilisés d’Apache.
# apt-get install php7.2-xml php7.2-curl php7.2-gd php7.2-mbstring
# apt-get install php7.2-bz2 php7.2-zip php7.2-json php7.2-readline
Activer Apache mod_ssl.
Activer Apache mod_rewrite.
Editez le fichier apache2.conf.
# a2enmod ssl
# a2enmod rewrite
# vi /etc/apache2/apache2.conf
Ajoutez les lignes suivantes à la fin de apache2.conf
<Directory /var/www/html>
AllowOverride All
</Directory>
Redémarrez le service Apache.
# service apache2 restart
Vous avez terminé l’installation du serveur Web Apache sur Ubuntu Linux.
Configuration des Hôtes Virtuels Apache
Hôtes virtuels: fonctionnalité permettant à un serveur Apache de proposer plusieurs sites Web utilisant la même adresse IP.
Permet de créer l’infrastructure nécessaire pour utiliser la fonctionnalité Apache VirtualHosts.
# mkdir /websites/mining-pool
# cd /websites/mining-pool
# mkdir www logs
# chown www-data.www-data /websites -R
Notre site Web s’appellera mining-pool.ninja.
Les fichiers du site Web mining-pool.ninja doivent se trouver dans le répertoire / websites / mining-pool / www.
Les journaux mining-pool.ninja seront stockés dans le répertoire / websites / mining-pool / logs.
Alert!
You need to change your configuration files to reflect your website name.
Créez un fichier de configuration Apache Virtualhost sur votre site Web.
# vi /etc/apache2/sites-available/mining-pool.conf
Voici le fichier avec notre configuration.
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerAdmin nobody@care.com
DocumentRoot /websites/mining-pool/www
ServerName mining-pool.ninja
<Directory /websites/mining-pool/www/>
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks
AllowOverride All
Require all granted
</Directory>
ErrorLog /websites/mining-pool/logs/error.log
CustomLog /websites/mining-pool/logs/access.log combined
LogLevel error
</VirtualHost>
Activez le fichier de configuration de votre site Web Virtualhost.
Redémarrez le service Apache.
# a2ensite mining-pool.conf
# service apache2 restart
Vous avez terminé la configuration Apache VirtualHosts.
Configuration du Registre de Domaine DNS
Accéder au GODADDY et achetez un domaine DNS.
Dans notre exemple, nous achetons le domaine nommé MINING-POOL.NINJA.
Vous pouvez utiliser n’importe quel site Web pour acheter un domaine DNS. GoDaddy n’est que mon choix personnel.
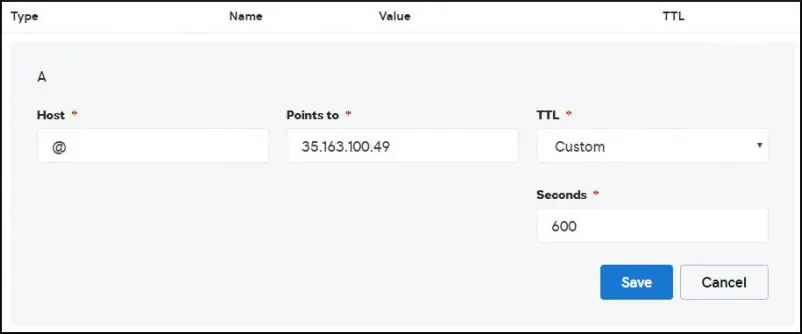
Créez une entrée DNS pointant votre site Web vers l’ordinateur exécutant Apache.
Dans notre exemple, nous avons créé une entrée DNS pointant le domaine MINING-POOL.NINJA vers l’adresse IP 35.163.100.49.
Utilisez la commande NSLOOKUP pour tester votre configuration DNS
# apt-get update
# apt-get install dnsutils
# nslookup mining-pool.ninja
Non-authoritative answer:
Name: mining-pool.ninja
Address: 35.163.100.49
Vous avez terminé la configuration du domaine DNS.
Ouvrez votre navigateur et essayez d’accéder à la version HTTP de votre site web.
Dans notre exemple, l’URL suivante a été entrée dans le navigateur:
• http://mining-pool.ninja
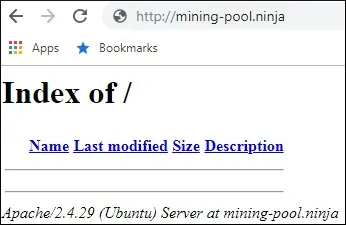
Notre seul souci est maintenant d’installer le certificat HTTPS gratuit et de rediriger automatiquement tout le trafic HTTP vers la version HTTPS de notre site Web.
Configuration du Certificat HTTPS Gratuit sur Apache
Installez les packages requis pour utiliser les certificats SSL / TLS libres de LET’S ENCRYPT sur Ubuntu Linux
# apt-get install software-properties-common
# add-apt-repository universe
# add-apt-repository ppa:certbot/certbot
# apt-get update
# apt-get install python-certbot-apache
Demandez et installez le certificat HTTPS gratuit Apache.
# certbot –apache -d mining-pool.ninja
• Appuyez sur (A) pour accepter les conditions d’utilisation.
• Appuyez sur (Y) pour partager votre courrier électronique et recevoir des lettres d’information.
• Appuyez sur (2) pour rediriger automatiquement votre site Web HTTP vers les versions HTTPS.
Saving debug log to /var/log/letsencrypt/letsencrypt.log
Plugins selected: Authenticator apache, Installer apache
Enter email address (used for urgent renewal and security notices) (Enter ‘c’ to
cancel): techexpert.tips@gmail.com
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
Please read the Terms of Service at
https://letsencrypt.org/documents/LE-SA-v1.2-November-15-2017.pdf. You must
agree in order to register with the ACME server at
https://acme-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
(A)gree/(C)ancel: A
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
Would you be willing to share your email address with the Electronic Frontier
Foundation, a founding partner of the Let’s Encrypt project and the non-profit
organization that develops Certbot? We’d like to send you email about our work
encrypting the web, EFF news, campaigns, and ways to support digital freedom.
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
(Y)es/(N)o: Y
Obtaining a new certificate
Performing the following challenges:
http-01 challenge for mining-pool.ninja
Enabled Apache rewrite module
Waiting for verification…
Cleaning up challenges
Created an SSL vhost at /etc/apache2/sites-available/mining-pool-le-ssl.conf
Enabled Apache socache_shmcb module
Enabled Apache ssl module
Deploying Certificate to VirtualHost /etc/apache2/sites-available/mining-pool-le-ssl.conf
Enabling available site: /etc/apache2/sites-available/mining-pool-le-ssl.conf
Please choose whether or not to redirect HTTP traffic to HTTPS, removing HTTP access.
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
1: No redirect – Make no further changes to the webserver configuration.
2: Redirect – Make all requests redirect to secure HTTPS access. Choose this for
new sites, or if you’re confident your site works on HTTPS. You can undo this
change by editing your web server’s configuration.
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
Select the appropriate number [1-2] then [enter] (press ‘c’ to cancel): 2
Enabled Apache rewrite module
Redirecting vhost in /etc/apache2/sites-enabled/mining-pool.conf to ssl vhost in /etc/apache2/sites-available/mining-pool-le-ssl.conf
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
Congratulations! You have successfully enabled https://mining-pool.ninja
You should test your configuration at:
https://www.ssllabs.com/ssltest/analyze.html?d=mining-pool.ninja
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
IMPORTANT NOTES:
– Congratulations! Your certificate and chain have been saved at:
/etc/letsencrypt/live/mining-pool.ninja/fullchain.pem
Your key file has been saved at:
/etc/letsencrypt/live/mining-pool.ninja/privkey.pem
Your cert will expire on 2019-03-19. To obtain a new or tweaked
version of this certificate in the future, simply run certbot again
with the « certonly » option. To non-interactively renew *all* of
your certificates, run « certbot renew »
– If you like Certbot, please consider supporting our work by:
Donating to ISRG / Let’s Encrypt: https://letsencrypt.org/donate
Donating to EFF: https://eff.org/donate-le
Le système demandera automatiquement le certificat gratuit.
Il configurera également votre serveur Web Apache pour qu’il redirige tous les accès HTTP vers la version HTTPS de votre site Web.
Dans notre exemple, le système a créé un fichier de configuration HTTPS Virtualhost nommé mining-pool-le-ssl.conf.
Voici le contenu du fichier de configuration HTTPS Virtualhost mining-pool-le-ssl.conf:
<IfModule mod_ssl.c>
<VirtualHost *:443>
ServerAdmin nobody@care.com
DocumentRoot /websites/www
ServerName mining-pool.ninja
<Directory /websites/www/>
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks
AllowOverride All
Require all granted
</Directory>
ErrorLog /websites/logs/error.log
CustomLog /websites/logs/access.log combined
LogLevel error
SSLCertificateFile /etc/letsencrypt/live/mining-pool.ninja/fullchain.pem
SSLCertificateKeyFile /etc/letsencrypt/live/mining-pool.ninja/privkey.pem
Include /etc/letsencrypt/options-ssl-apache.conf
</VirtualHost>
</IfModule>
Le fichier KEY contient votre clé privée de certificat et doit être gardé dans un endroit sûr tout le temps.
Le fichier de clé de mining-pool.ninja était stocké dans /etc/letsencrypt/live/mining-pool.ninja/privkey.pem.
Le système modifie automatiquement le fichier de configuration Apache Virtualhost d’origine.
Toutes les requêtes HTTP seront automatiquement redirigées vers la version HTTPS de votre site Web.
Voici le contenu du fichier de configuration HTTP Virtualhost d’origine mis à jour, mining-pool.conf:
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerAdmin nobody@care.com
DocumentRoot /websites/www
ServerName mining-pool.ninja
<Directory /websites/www/>
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks
AllowOverride All
Require all granted
</Directory>
ErrorLog /websites/logs/error.log
CustomLog /websites/logs/access.log combined
LogLevel error
RewriteEngine on
RewriteCond %{SERVER_NAME} =mining-pool.ninja
RewriteRule ^ https://%{SERVER_NAME}%{REQUEST_URI} [END,NE,R=permanent]
</VirtualHost>
Test du Certificat HTTPS Gratuit sur Apache
Toute la configuration requise est terminée.
Il est temps de tester votre configuration.
Ouvrez votre navigateur et essayez d’accéder à la version HTTP de votre site web.
Dans notre exemple, l’URL suivante a été entrée dans le navigateur:
• http://mining-pool.ninja
Apache redirigera automatiquement la requête HTTP vers la version HTTPS de votre site Web.
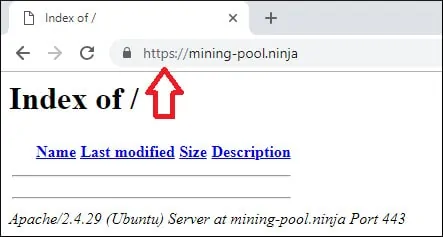
Vous avez terminé la configuration du certificat libre Apache HTTPS.
Comment Renouveler le Certificat HTTPS Gratuit
Les certificats SSL / TLS LET’S ENCRYPT Free ne sont valides que pendant 90 jours.
Le système crée une tâche planifiée pour renouveler automatiquement tout certificat dans les trente jours suivant l’expiration.
Le nom de la tâche planifiée est certbot et il se trouve dans le répertoire /etc/cron.d.
Voici le contenu du fichier /etc/cron.d/certbot:
# /etc/cron.d/certbot: crontab entries for the certbot package
#
# Upstream recommends attempting renewal twice a day
#
# Eventually, this will be an opportunity to validate certificates
# haven’t been revoked, etc. Renewal will only occur if expiration
# is within 30 days.
#
# Important Note! This cronjob will NOT be executed if you are
# running systemd as your init system. If you are running systemd,
# the cronjob.timer function takes precedence over this cronjob. For
# more details, see the systemd.timer manpage, or use systemctl show
# certbot.timer.
SHELL=/bin/sh
PATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin
0 */12 * * * root test -x /usr/bin/certbot -a ! -d /run/systemd/system && perl -e ‘sleep int(rand(43200))’ && certbot -q renew
Utilisez la commande suivante pour simuler le processus de renouvellement du certificat.
# certbot renew –dry-run
Vous devriez voir les messages suivants:
Saving debug log to /var/log/letsencrypt/letsencrypt.log
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
Processing /etc/letsencrypt/renewal/mining-pool.ninja.conf
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
Cert not due for renewal, but simulating renewal for dry run
Plugins selected: Authenticator apache, Installer apache
Renewing an existing certificate
Performing the following challenges:
http-01 challenge for mining-pool.ninja
Waiting for verification…
Cleaning up challenges
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
new certificate deployed with reload of apache server; fullchain is
/etc/letsencrypt/live/mining-pool.ninja/fullchain.pem
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
** DRY RUN: simulating ‘certbot renew’ close to cert expiry
** (The test certificates below have not been saved.)
Congratulations, all renewals succeeded. The following certs have been renewed:
/etc/letsencrypt/live/mining-pool.ninja/fullchain.pem (success)
** DRY RUN: simulating ‘certbot renew’ close to cert expiry
** (The test certificates above have not been saved.)
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
IMPORTANT NOTES:
– Your account credentials have been saved in your Certbot
configuration directory at /etc/letsencrypt. You should make a
secure backup of this folder now. This configuration directory will
also contain certificates and private keys obtained by Certbot so
making regular backups of this folder is ideal.
Leave A Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.